Tech Explained: Which LED Bulbs Are Best?
LED bulbs like these aren't actually DESIGNED for headlight applications specifically - they are simply designed as universal bulb replacements that do their best to mimic the function of a halogen automotive light bulb.
Sometimes these bulbs are used in headlights, other times fog lights, other times on boats, ATV/UTV, industrial vehicles and more. Before you dive into the world of LED bulb upgrades, get your facts straight! No matter how much better 1 bulb style is than another, keep in mind that none of them are currently street legal for use on roads in the USA. There are plenty of applications where they're fine to use like fog lights, a dedicated off-road application and more, but make sure you're following the rules! For information on LED bulb street usage click here.
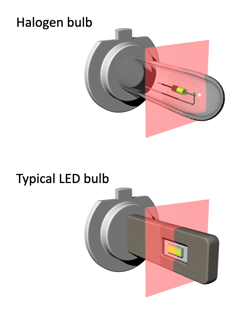 |
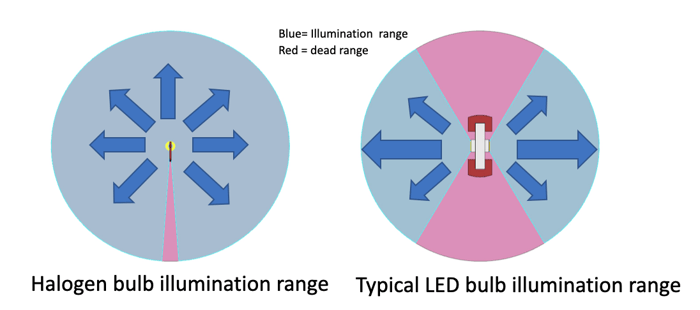
Halogen bulbs are similar to most light bulbs. Other than the filament support wire shadow, it illuminates near Typical LED bulbs have 2 LEDs facing out, with the center divided by the PCB and body. LEDs are a surface lighting device, typically carrying a Lambertian distribution at 50% or around 120 degrees. |
Optics Basics
There are two types of optics commonly used for Low beams: Reflector and Projector. Reflector type optics categorize into Single focus optics (low beam only)and Dual-focus optics(segmented for low beam and high beam usage).
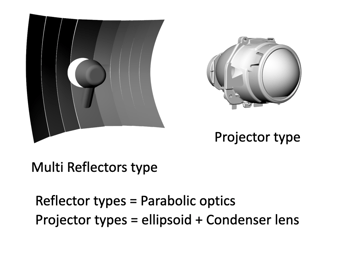 |
Reflector Type Reflector types = Parabolic optics Projector types = ellipsoid + Condenser lens |
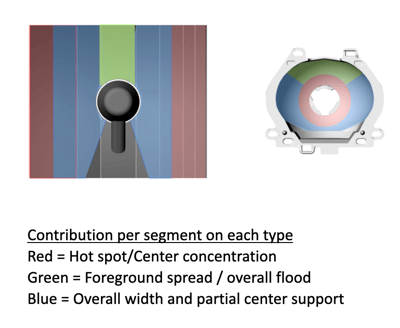
Understand the Challenges of LED bulb Performance
We learned directly above the illumination range with typical LED bulb configuration is the "dead angle" range.
In reflector optics, this results in a lack of proper foreground illumination or overall flood range. Projector headlights require proper illumination to protect from insufficient beam center intensity and bottom foreground illumination.
This design flaw exists in any LED bulb that has 2 LEDs facing out.
H4 Specific Dual Focus Reflector
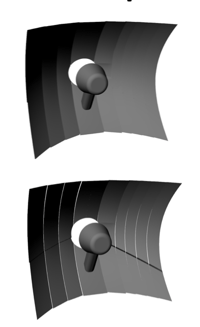 |
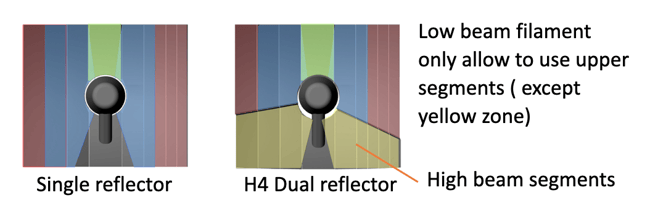
Single focus reflector H11H7 HB4 etc Dual focus reflector H4 (one Halogen bulb functions as both low beam and high beam = 2 filament in one bulb) |
H4 dual reflector has two segments: upper half creates low beam with cutoff, and Bottom elements are for high beam. For the H4 bulb's low beam, the filament will not illuminate the high beam. The H4 bulb is designed with a glare control shade shield.
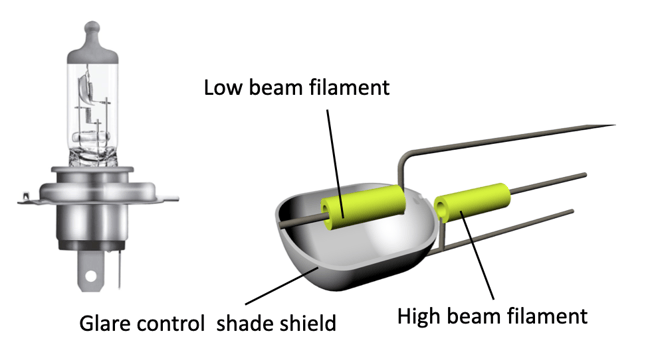
H4 Halogen Bulb Specification
With the shade shield cup blocking the lower illumination angle, the H4 bulb's low beam filament can safely and selectively illuminate the blue-colored area (image below).
Since filament has a 1.4mm diameter, rays from the filament peak can reach a slightly lower angle than the primary ray group. Yellow is a marginal region to accept such a group.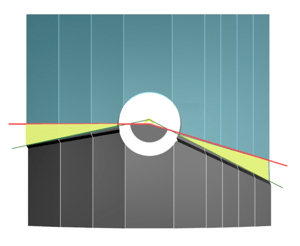 Target illumination distribution
Target illumination distribution
Blue = target region
Yellow = allowance region
Ideal H4 illumination distribution shall look like the Blue-highlighted zone (above).
H4 LED Bulb's Adoption
The goal is not to create glare. All aftermarket H4 LED bulbs are equipped with shade cups, but the problem is an unregulated LED chip, and shade cup placing does not ensure proper glare cut. 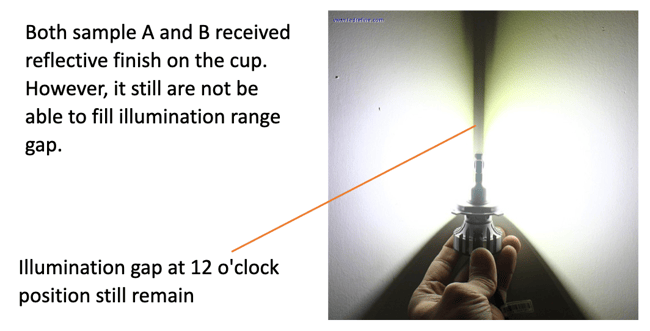
Generally, shade cups receive the light created by reflections, which some say enhances illumination efficiency, but none of the products aim to fill the illumination range. They are bouncing the reflection around, which does not optically illuminate the target surface.
Both samples A and B received a reflective finish on the cup. However, it still does not fill the illumination range gap.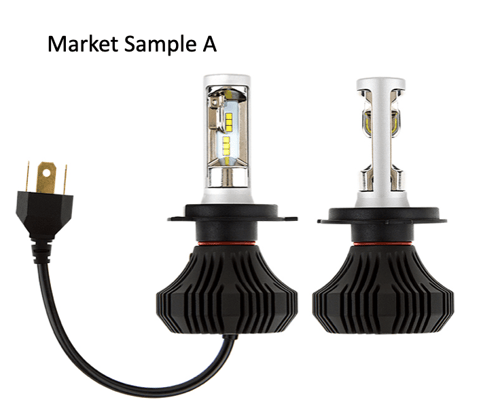
2Stroke 3.0 H4 Innovative Reflector Shade Cup
Since the product misses the 12 o'clock illumination range, there's a lack of foreground illumination spread. Not many bulbs control glare properly (LED chip selection is improper), and the reflector can not utilize unregulated reflections.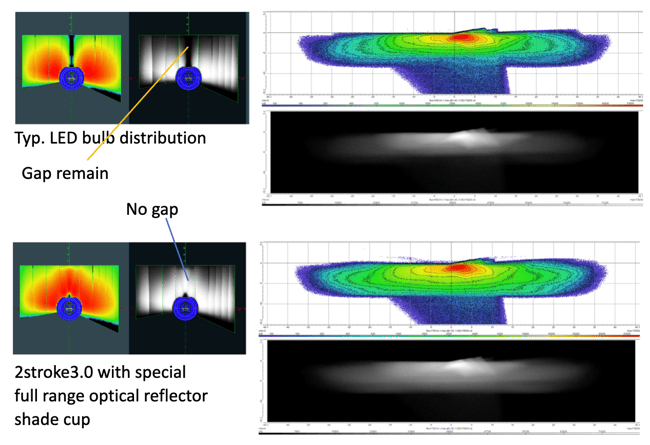
The 2stroke 3.0 H4's special reflector cups create a secondary virtual lighting point using an ellipsoid reflector built into the shade cup. While they safely prevent undesired glare, they also RECYCLE stray range rays into an optically controlled illumination range gap filler.
Unique Design Detail
Reflection image size and position proximity accurately reflect the actual first light-emitting surface size. Virtual lighting points aim right next to the low beam LED chipset area. 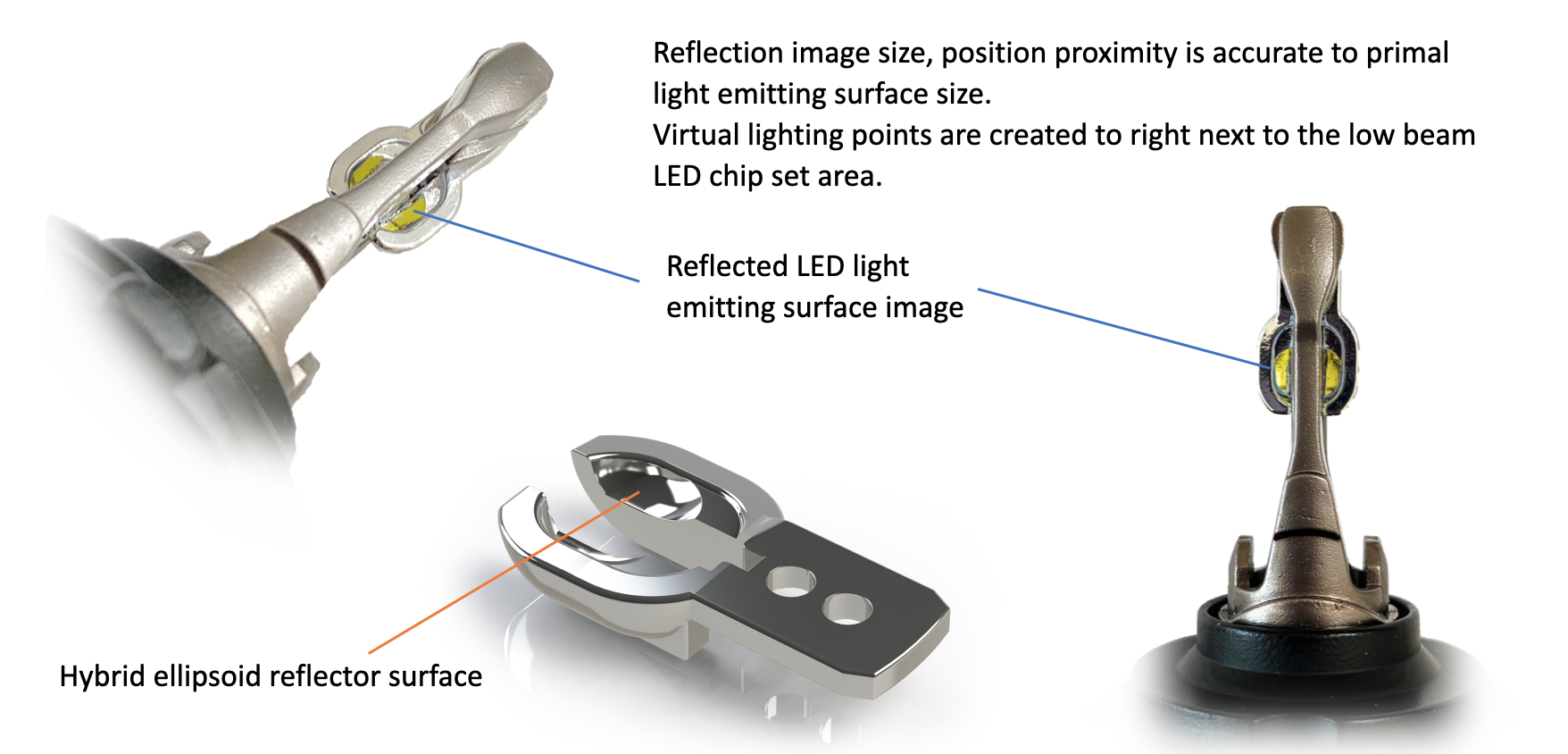
Ellipsoid Reflector Surface
 |
|
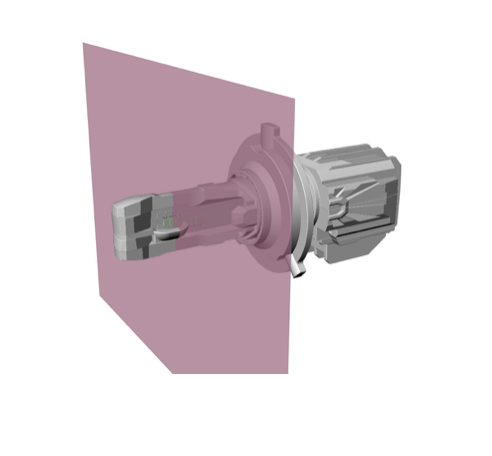
| An Ellipsoid reflector focuses light rays from one focus point to another. The 2stroke 3.0 H4 bulb uses a modified adjusted ellipsoid reflector integrated into the inside wall of the shade cup, which creates a secondary virtual lighting point outside of the LED emission surface. | Since the current LED bulb design has a center-divided configuration, and PCB and LED bulb bodies are located directly on the Y axis, a secondary virtual illumination point must be outside the Y-axis. However, it must be as close as a first illumination point. |
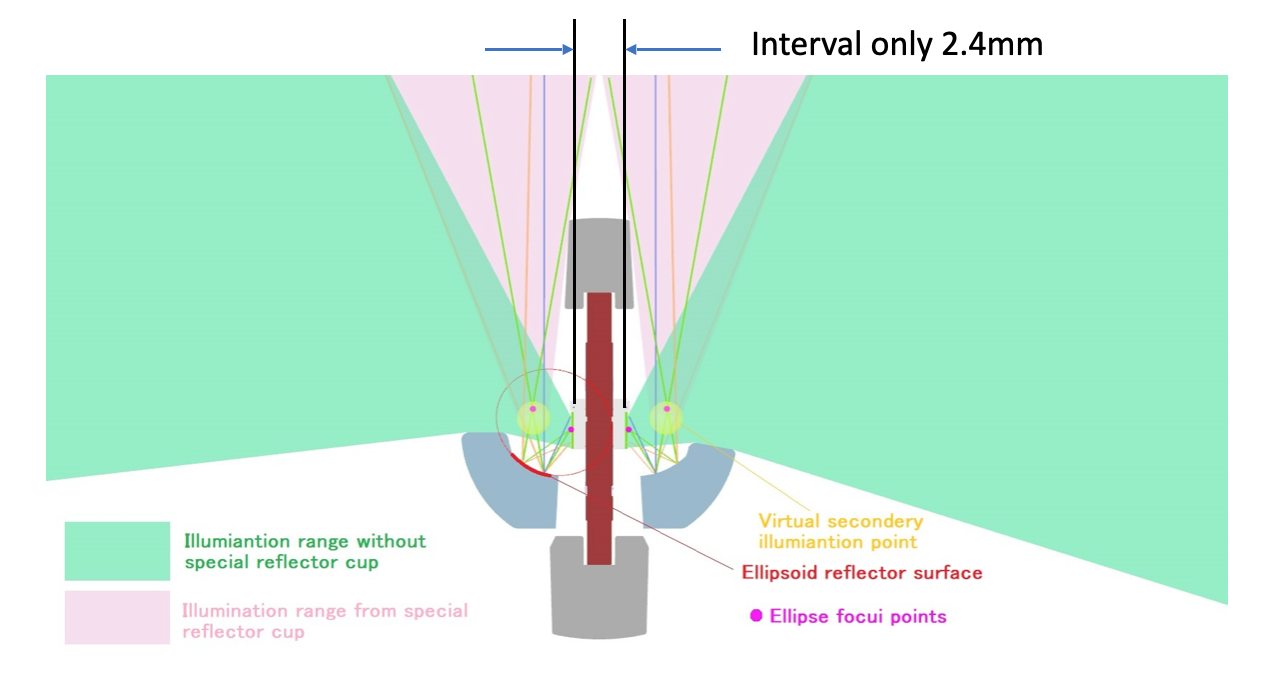
The second virtual illumination point size needs to be the same as the first light-emitting surface because the optics are designed based on the H4 halogen filament illumination character. 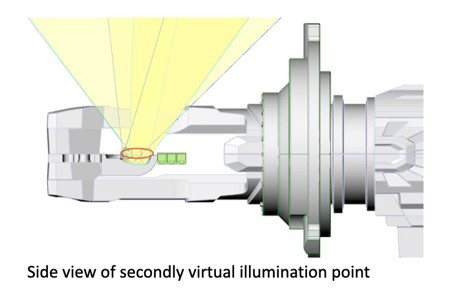
The red circle shows the second virtual illumination point. The size of the visual illumination point is consistent with the first light-emitting surface area size. Failure to meet this size limitation can result in undesired glare or beam scatter.
This unique virtual illumination point generator can be only possible with the 2stroke 3.0's unique cooling system, which allows LED's light-emitting surface interval to be only 2.4mm( thinnest in Market * single filament model is as light as 2.0mm)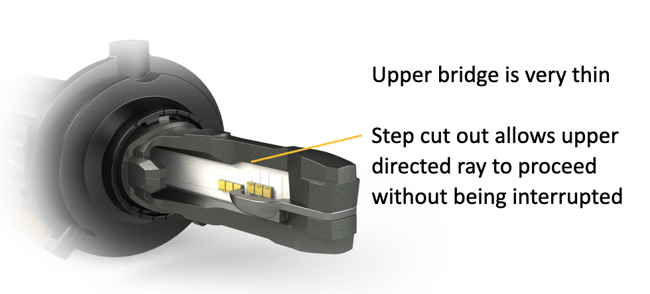
Unlike other LED bulbs that rely on the heatsink for thermal conductivity and front bridge material conduction, our unique cooling system uses the PCB itself as one of the central heatsink fins, which allows the bridge to be much thinner.
Q&A
Is the 2Stroke 3.0 brighter than Ultra 2?
The 2Stroke 3.0's lighting output is about 40% less than the Ultra2, but it has an unbeatable focus that contributes to road illumination that often exceeds Ultra2, especially in smaller to mid-sized reflector housing.
For larger (horizontally longer, larger) reflector housings, the Ultra2 or SV4 (or other higher raw lumen bulb) excels.
I do not hesitate to suggest Ultra2 and SV4 for larger optics while also weighing the pros and cons of either.
2Stroke 3.0 will remain top in terms of beam quality regardless of optics.
How Do I Properly Measure Lux?
Lux reading only can be a valid reference IF measured in the same distance and measured at the same measuring spot in the same optics system. For example, at 10m, the Lux rating maybe 500 lux but becomes only 347 lux at 12m. (Want to know more about the difference between Lux and Lumen? Check out this blog.)
Having higher lux in one optics does not mean it will have higher lux in another housing. The Lux rating will vary with certain applications and distance measurements.
The proper answer is:
In low beam reflector optics of vehicle ____ measured at a distance of ___m ( or feet), measured spot 0.86 degrees down 1.3 degrees to the right ( distance measuring spot), it measured ___ lux.
Only 2,100lm (2,600lm initial)? There are so many bulbs rated higher!
2,100lm is the minimum output number in a heated, controlled environment. Many LED bulbs advertise a theoretical absolute max number but won't tell you the actual outputting lumen.
2ST3 was run in a 60C(140F) heated oven for 1 hour and then measured in a device called an integrated sphere to assure the minimum of 2,100lm is outputting.
In theory, max output from a 2 x HKL351.TE emitter can be 4,800lm (If we want to state lumen rating as most cheap LED bulbs packaging describes).
Unless it is measured in proper equipment, lumen rating is a volatile marketing number. It is OK to admit that there are actually higher lumen outputting bulbs. We did not choose that fight because the Ultra 2 and SV4 have much more depth in true optical strength.
How does the 2Stroke 3.0 lux measure have a higher output than Ultra2 or SV4 in some housings?
This is because the lumen density of LED is much higher than the other two. HKL531.TE emitter has a near-identical size of filament emission area.
Ultra 2 has about 2.5 times larger chip area compare to HKL531.TE Ultra 2 1,750lm from 11.6mm2
Lumen density 150lm/mm2 2ST3 1,050lm from 4.46mm 235lm/mm2 filament ortho view box size is 6.3mm2 per side (if observed as 2 sided right and left selected view)
At 3 and 6 o'clock, illumination can be observed as effective in the Ultra 2, similar to having filament outputting 6.3mm2 x 150lm(per side) x 2 total 1,890lm.
2Stroke 3.0 efficacy is similar to Ultra 2, having filament output at 6.3mm2 x 235lm(per side) x 2 total 2,961lm.
For a larger chip LED bulb like Ultra2, a near filament-sized box is illuminated as an accidental overlay that overlaps the intended beam pattern. The amount of overlap is uncertain; some overlap adds intensity, some do not, and they cannot gain intensity. That is the probability difference you see in a variety of optics with large housing.
Some halogen bulbs output 2,100lm+ at working voltage (14.4V); how does 2Stroke 3.0 compare to it?
A5: 2Stroke 3.0 chip area itself is smaller than the halogen filament overall ortho view box. In the center, 80% of filament has the highest output in halogen, and the 2Stroke 3.0 chip duplicates this CRITICAL illuminance area size of the filament. The LED chip is generally larger than the halogen filament but not in the 2Stroke 3.0 case. The 2Stroke 3.0 chip packed all lumens within the critical center at 80% of the filament size.
Also, the LED typically shoots stronger illumination at a straight angle, while the filament is full 360-degree illumination. This is a disadvantage in terms of the full-beam distribution range. In the reflector housing's case, the 2Stroke 3.0 shoots a much stronger beam because of this angle limitation. The outer segment of the reflector handles a hot spot of beam distribution. The 2Stroke 3.0 LED chip has a relatively higher output ratio into 3 and 9 o'clock (the hotspot's corresponding reflector segment), resulting in a much higher beam center focus, even from the same lumen outputting halogen bulb.
Con: The lack of foreground illumination. Directly above the segment handle, there's a lower angle flood beam in the reflector.
Does the 2Stroke 3 work well in projector housing?
Much less efficient compare to a reflector. In projector optics, the hot spot is handled by the center back area of the reflector bowl, where all LED bulbs fail to illuminate directly above because of the shadow at 6 o'clock illumination).
Some projectors are composed of beams using an "overlap" construction. Some larger chip LED bulbs may positively (accidentally) achieve higher beam center focus due to this effect.
Projector performance will be case by case. However, how the beam center overlap is designed will determine how effectively the 2Stroke 3.0 can perform in a projector.
Will dust get in the internal circulation cooling?
No. It is a fully internal closed-loop circulation. However, it is critically important that the customer "seal the housing" if the headlamp comes with a dust cap cover. It must be advised as a "warning" not to use the 2Stroke 3.0 bulb if the customer cannot properly install the dust cover. Leaving an opening will cause dust to enter the headlamp, and the bulb can blow the dust around inside. This is not a product-level issue since headlamp housing never should be left open, but I can see some customers using it without a dust cap or cover.
If dust cover incompatibility is reported, suggest a compatible-sized rubber dust cover along with the product recommendation.
What is the tension spring on the H11 bulb?
The tension spring creates a specification defined downward retaining force of 5Nm. The bulb insert is slightly larger than the bulb base diameter for installation tolerance. Other than the H11 type of bulb(H13 also supposed to have a tension spring but did not make it this time), the self-gasketing bulb has an o-ring gasket around the bulb base collar, and it goes into the bulb insert opening to fill the gap.
However, the H11 gasket pushes against the flat surface of the bulb insert opening rather than filling the gap between the bulb base and bulb insert opening inner wall. The H11 bulb cannot self-align the optical reference center without a tension spring. By the tension spring pushing the bulb downward, it makes the bottom surface of the bulb base align to the bottom surface of the bulb insert opening, which ensures proper alignment.
This is essential, especially because we use the high-precision LED chip.
2st3.0 is the ONLY LED bulb with a rotatable bulb base collar WITH specification defined tension spring equipped.
Why are there geared adjustable bulb base collar and 3 x friction o-ring type bulb base collar?
A Twist-lock type bulb uses a geared-step adjustable bulb base collar. Due to design limitations, there is a dead-angle (where the entrance angles) in the geared step adjustable type. We will monitor market popularity feedback and may add an optional in-between angle collar.
For spring retainer install types (such as H7, H4, etc.), bulb base collars are full-range free rotation. The position is retained by triple friction o-ring gasket inside.
This video also does a good job at offering a high-level overview of the technology explained here:
.png)



































